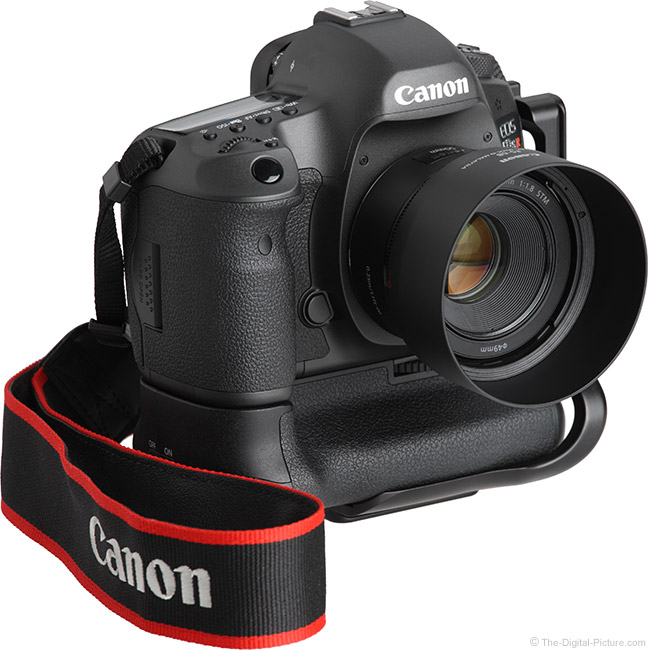
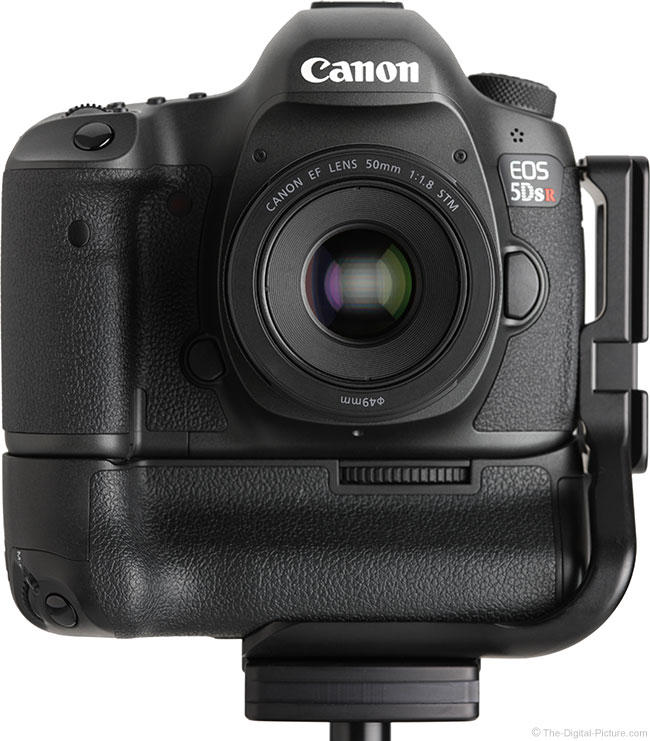
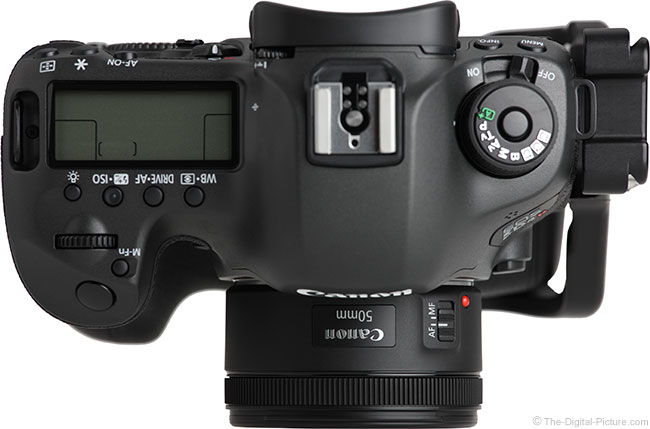
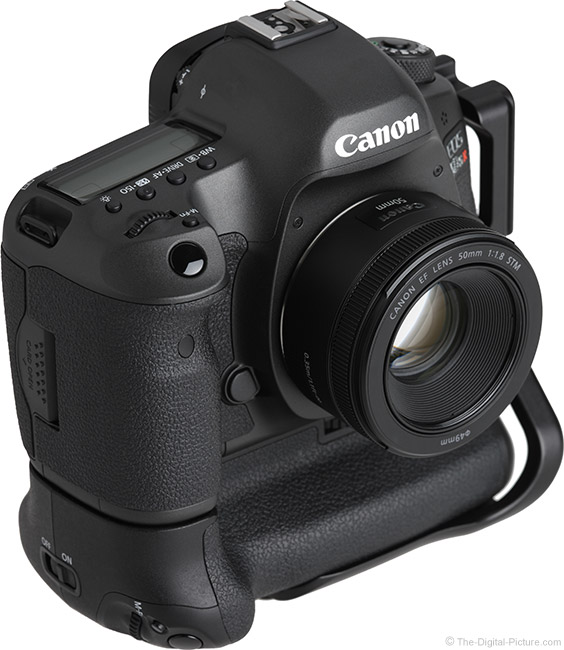
Canon celebrated the 25th year anniversary of the
EF 50mm f/1.8 II Lens with ... the announcement of its replacement, the Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens. The 50mm f/1.8 II was an extremely popular lens, primarily because of its introduction-to-prime-wide aperture and good stopped-down image quality at a very low price. Many had long been waiting for a new 50mm lens from Canon and the 50mm STM Lens appeared to be a significant upgrade while retaining essentially the same ultra-small size and weight. That the new lens remained Canon's lowest-priced definitely produced smiles.
The image below shows the visual differences between the 50 f/1.8 STM (sandwiched in the middle) and the 50 f/1.8 II.
The poorly-constructed 50mm f/1.8 II left many opportunities for upgrades and the 50mm f/1.8 STM addressed a substantial number of them. Here is a list of some differences between these lenses:
- 7 rounded aperture blades vs. 5 non-rounded (no more pentagonal bokeh)
- Metal lens mount vs. plastic
- Improved overall build quality (my original 50mm f/1.8 II broke in half for an unknown reason)
- Super Spectra Coating
- A much improved manual focus ring
- STM vs. Micro Motor (smoother and quieter)
- FTM (Full Time Manual) focusing (as long as shutter release is half-pressed)
- 13.8" (350mm) MFD (Minimum Focus Distance) vs. 17.7" (450mm)
- 0.21x MM (Maximum Magnification) vs. 0.15x
- 49mm vs. 52mm filter size (though not much of an advantage from my perspective)
- Narrower f/22 aperture available vs. f/16
- Accepts normal bayonet-mount lens hood vs. threaded adapter
Focal Length / Focal Length Range
Sometimes, it is easy to justify the purchase of a lens for a subset of its attributes (such as price), but when it is time to select the ideal lens for a particular use, the focal length always becomes a very important attribute. The focal length determines the angle of view which determines the distance required for the desired subject framing and the distance from the subject determines the perspective. Fortunately for this lens, the 50mm focal length has a great number of uses.
On a full frame body, a 50mm focal length appears very natural, approximating how we perceive a scene with our own eyes in field of view and perspective terms. In the film days, a 50mm lens was often available in a 35mm SLR kit, indicating both this focal length's popularity and its general purpose usefulness. While not available in manufacturers' kits today, Canon and Nikon both have four 50mm prime lenses in their lineups, showing the continued popularity of this focal length.
Fifty mm lenses are frequently used in fashion, portraiture, weddings, documentary, lifestyle, sports, architecture, landscape and general studio photography applications including product photography. As noted, a number of the good applications for this lens include people as subjects. A 50mm lens used on a full frame body is modestly too wide angle for tightly framed head shot portraits (a too-close perspective is required for my taste at least), but 50mm is a very good choice for less-tightly-framed head and shoulders, partial body and full body portraits.
Mounted on an APS-C/1.6x
FOVCF body, a 50mm lens delivers an angle of view equivalent to an 80mm lens on a full frame body. This tighter angle of view is useful for the same purposes just mentioned and tighter-framed portraits retain a better perspective.
The 50mm focal length can work well for panorama images. I was out in the boat giving the 50 STM some real world use when this iron railroad bridge being lit by a setting sun caught my eye. I captured portions of the bridge in many images, but decided to capture a series of images that could be used for a panorama (which also allowed many sub-images to be cropped out later). The current was moving the boat, so I quickly captured the 10 frames used for creating this 95 megapixel image with a
Canon EOS 5D Mark III behind the 50 STM:
Max Aperture
A feature that many prime (fixed focal length) lenses have is an ultra-wide aperture. A wide aperture allows more light to reach the imaging sensor, permitting action-stopping shutter speeds in low light conditions. A wide aperture also reduces depth of field (DOF), permitting a strong background blur to be created. Here is an example created with the full frame
Canon EOS 5Ds R:
The depth of field continues to increase as the aperture narrows beyond f/8, but the change is not noticeable at this resolution. Just because the lens opens to f/1.8 doesn't mean that you will want to use the lens at f/1.8 for all purposes.
The shallow DOF may not work well for the subject and/or, the image quality at the widest aperture may not be acceptable.
Image Quality
When the 50 f/1.8 STM was announced, I was comparing the MTF chart against it predecessor, the 50 f/1.8 II. I initially thought I had downloaded one of the wrong charts. The graphs were sized differently, but they were showing the identical line plot.
I of course could not mentally rest without knowing what was going on, so I asked. In answer to my "Does the new 50mm STM contain the same optics design as the 50mm f/1.8 II?" question, Canon U.S.A.'s extremely knowledgeable Chuck Westfall responded:
"Yes, the optics of the EF 50mm f/1.8 STM are the same as the original EF 50mm f/1.8 and EF 50mm f/1.8 II."
Was I disappointed? Yes. I of course want all new lenses to be optically improved over the prior version. Is using the same optical design in the new lens a bad decision on Canon's part? No, not necessarily. People loved the 50mm f/1.8 II Lens, otherwise known as the "Nifty Fifty", especially because of the decent prime-grade image quality it delivered (when stopped down) at a really low price tag. With a host of improvements available at the same price point, the STM version would launch to instant success.
In addition, Canon promised "optimized lens placement and Super Spectra Coating (SSC), translating into less ghosting and flaring than the previous model, while at the same time helping to enhance light transmission and optimize color reproduction accuracy."
One of the key reasons to select a prime lens over a zoom is to get a wider aperture. However, in this case, you may not want to use the widest apertures available if sharp results are your goal. At f/1.8, I'll call the 50 STM results ... artistic. A small area in the center of the frame has just-usable sharpness (needs extra contrast/de-haze and sharpening), but the balance of the image circle is blurry with an overall low contrast fog/haze present.
Would I use f/1.8 on this lens? Not if I was looking for sharp results. However, photographers are paying a lot of money for lenses that intentionally create a dreamy look such as this. With this lens, you can dial in the amount of effect by simply selecting a wider aperture.
At f/2, the center of the frame shows a marked improvement in sharpness, but the balance of the frame shows more improvement at f/2.8. At f/2.8 the center is very sharp, the mid-frame portion of the image circle is reasonably sharp and corners, while improved, remain rather soft. Note that APS-C format body users will avoid the worst of this lens' corner softness.
At f/4, this lens looks very impressive with the area of sharpness progressing strongly outward in the image circle and only the extreme full frame corners showing softness. Full frame corner sharpness continues to improve as the aperture narrows, with f/8 and f/11 corners looking excellent.
As always, the effects of diffraction become noticeable at the narrowest apertures with all current DSLR models showing reduced sharpness at f/16 and results are quite soft at f/22 even on a full frame 22mp DSLR. That this lens now features f/22 (vs. the II's narrowest f/16 aperture) means little to me personally.
I recommend viewing the
Canon 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens image quality results to see the sharpness performance with your own eyes. Also available in this tool is the
50mm f/1.8 STM vs. II lens comparison. Using the 5Ds R as a test body, we see that the STM is slightly sharper in the center of the frame at f/1.8. By f/2.8, the two lenses appear to be equivalents. Stopping down to f/4 and beyond shows the STM lens to have a nice advantage in the mid and peripheral portions of the image circle.
Here is a real world set of sharpness examples. These crops were taken from just slightly above the bottom right corner of a full frame
Canon EOS 5D Mark III-captured images.
RAW format images were processed in DPP using the Standard Picture Style with sharpness level set to "1". The corner of the frame always brings out the worst in a lens and as expected, this lens shows soft, hazy details at the wider apertures.
Also commonly showing in wide aperture corners is vignetting. With roughly 1.5 stops of vignetting showing in full frame corners at f/1.8, the 50 STM's darkening is noticeable. But, this amount is rather low from a wide aperture prime comparison perspective (I had to double check to make sure that vignetting correction was not enabled for these results). By f/2.8, the corner shading is down to about .5 stops and it continues to decrease until essentially gone at f/4. Those using an APS-C format DSLR will notice very little vignetting from this lens even when used at f/1.8
The most frequently seen type of CA (Chromatic Aberration), lateral (or transverse) CA, shows as different colors of the spectrum being magnified differently with the mid and especially in the periphery of the image circle showing color fringing at lines of strong contrast (where the greatest difference in wavelengths meet). This defect is generally easily correctable, but ... no correction is needed with this lens in front of the camera. The 50 f/1.8 STM performs very well, showing negligible lateral CA as show in this full frame corner crop:
The 50 f/1.8 STM's very low lens element/group count (6/5) results in only mild amounts of flare with the sun in the corner of the frame at wide apertures. Stop down to f/5.6 or beyond and flare becomes practically nonexistent.
Coma is generally recognized by sharp detail contrast towards the center of an image and long, soft contrast transition toward the image periphery. The 50 f/1.8 STM shows strong coma in the periphery of the image circle at the widest apertures. The coma slowly lessens as the aperture is narrowed until much diminished at f/4.
This lens has a slight amount of barrel distortion that will primarily show only when a straight line is running near and parallel to the edge of a full frame image.
While the wide open image quality this lens delivers may be described as "dreamy", the bokeh (quality of the out-of-focus portions of the image) would not fully qualify for the "creamy" descriptor by most. While I'm not going to call the 50 f/1.8 STM's bokeh special, it is not bad and the updated lens renders blurred portions of the image more pleasingly than its predecessor.
The most readily recognized difference is in the shape of the out of focus highlights. Basically, all lenses produce rounded out of focus specular highlights when used at their widest apertures (the aperture blades stay out of the picture). When stopped down, the lens' aperture design plays a larger role in the shapes with blade count being especially notable in this case.
The 50 f/1.8 II's 5-blade non-rounded design was noted for creating strong pentagonal shapes from out of focus highlights. The 50 f/1.8 STM's 7-blade aperture adds two sides to these shapes and the rounded blade shape softens the corners slightly. While the STM's results are much better than the sharp-pointed pentagonals, one should not expect perfectly round out of focus highlights at narrower apertures. Here is a comparison example that highlights the bokeh difference between the 50 f/1.8 STM and the 50 f/1.8 II lenses:
For many people, this lens is an introduction to prime lens image quality and part of that introduction is to the strong background blur that wide aperture prime lenses are generally capable of. At a short focus distance, the widest apertures of this lens can indeed create a strong background blur. I'll share an example later.
Overall, it is not hard to find flaws in the Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens' image quality. But stopped down, this lens performs very well. Especially for the price.
Focusing
The Canon EF 50 f/1.8 STM Lens name reveals the use of a stepping motor-driven AF system (the "STM" part). The STM design is a focus-by-wire AF implementation.
The focusing ring does not turn during AF and FTM (Full Time Manual) focusing is supported. In AF mode, manual focusing (FTM) is supported only while the shutter release is half-pressed, diminishing the pre-focus usefulness of FTM. When the menu option is available, electronic manual focusing of the lens must be enabled (the default).
Also not as friendly as Ring USM designs is that, in MF mode (switch in the "MF" position), the camera meter must be on/awake for manual focusing to function. Note that MF is not available during DOF preview.
Not surprising is that a small lens has an also-small focusing ring. The flush-mounted focus ring is usable with the image framing remaining stable (a nice upgrade from the f/1.8 II). The MF ring is easy to rotate and is smooth.
The rate of focusing change depends on how quickly the 50 STM focus ring is rotated. Turn the MF ring slowly for fine adjustments and quickly for a faster change. While I understand the reasoning for this, I find the differing rates to be slightly maddening. Move the ring too fast when fine tuning and you need to start over. I still prefer the linear change design.
Expect some modest subject size change in the frame when pulling focus using this lens.
The 50 STM's front filter threads do not rotate with focusing, facilitating use of
circular polarizer filters. This lens uses a front-focusing design and the lens' inner barrel extends modestly at minimum focus distance.
There are no focus distance or DOF markings provided on this lens. There is no room for a distance window, and since the focusing ring is not directly connected to the focusing gears (same as with most USM AF implementations), printed markings are not an option. Most AF lenses produced today have no significant DOF markings and I doubt that many using this lens will care about either of these missing features.
At review time, Canon's best lenses are currently getting ring USM AF systems and the rest are getting the STM option. Ring USM lenses typically focus faster and have advantages including always-available full time manual focusing (even with the camera powered off). An STM system's biggest advantage over ring USM (aside from low cost) is in the smoothness of focusing, primarily benefiting Movie Servo AF.
One of the biggest differences between the 50mm f/1.8 II and the 50mm f/1.8 STM lenses, as their names imply, is the AF system implementation and the audibility differences of these systems is especially notable. The 50mm f/1.8 STM's focusing sound is greatly improved/reduced over the 50mm f/1.8 II micro motor's presence-announcing buzz. Identical near full range autofocus adjustments in both directions can be heard in the following AF sound comparison clip. Turn up your speaker volume and then click on the visual comparison image:
The perfect lens AF sound would of course be a flat line, but ... AF moves parts and moving parts tend to make at least some noise. In this case, the STM is audible and audible enough for on-camera mics to pick up.
As with other STM lenses, a slow change in focus distance (such as when recording video) results in a noticeably quieter sound.
As usual, the 50 f/1.8 STM makes short focus distance changes quickly, but a full-extent focus adjustment provides time for the smoothness of focusing to be better appreciated.
From a speed comparison standpoint, both 50mm f/1.8 lenses focus with similar speed ... unless one or the other makes some adjustments post initial focus acquisition. The STM version did not make these adjustments as frequently in my testing, so it appears to be the faster focusing lens in practical use. AF speed is probably not going to be an upgrade reason for most.
I spent a good amount of time testing AF accuracy and the EF 50mm f/1.8 STM lens performs very well in this regard.
The Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens' 13.8" (350mm) MFD (Minimum Focus Distance) creates a best-in-class (omitting macro lenses) 0.21x MM (Maximum Magnification). These specs are notably improved over the 50 f/1.8 II. Here is a comparison:
Here is a real life 0.21x magnification example from a full frame camera:
The flower is about 2.5" (64mm) in diameter and near this lens' MFD. Also seen in this example is the strong background blur this lens can produce ... along with the marginal f/1.8 image quality at this distance. Taken at 1/1600 sec, there is no motion blur in this image.
Mounting an extension tube behind wide angle and normal focal length lenses can produce significantly reduced MFDs with the loss of distant focusing distances being a penalty. Add a
12mm extension tube for a magnification range of 0.45-0.24x and a
25mm extension tube provides a macro-approaching 0.74-0.53x spec.
This lens is not compatible with Canon Extenders.
Build Quality & Features
While this lens is nearly featureless from an external perspective, the engineering plastic design along with the metal lens mount (an upgrade from the II's plastic mount) appear solid. This is not weather-sealed construction. The other external components include a single switch, an extending inner lens barrel and a small, flush-set MF ring.
The MF ring has very little play/wobble in its design, but the extend inner lens barrel does move a bit when touched. There is no reason to touch it – except when installing the lens cap. The lens may retract when the lens cap is pressed on.
Here is a size and weight comparison table:
Here is a visual comparison of Canon's current 50mm prime lens models:
Positioned above from left to right in their fully retracted positions are the following lenses:
The same lenses are shown below with their lens hoods in place (the macro lens excluded).
Let's just say that the 50 STM will not block the light from your pop-up flash.
The Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens utilizes small 49mm filters. I'm not sure that a lens this inexpensive justifies a
protection filter, though I would be lost without
circular polarizer filters for all of my lenses and also frequently find
neutral density filters to be invaluable. For these filter types, the small 49mm size is reflected in relatively small prices. The small form factor means these filters are easy to take with you.
Unfortunately, there are no other lenses in the site's database of over 300 lenses that share this filter size. We do not even have a B+W test ring in the 49mm size. For most, filters for this lens will be dedicated. Alternatively, a
step-up ring, perhaps adapting 49mm to 52mm or 67mm, is a good option.
The
Canon ES-68 Lens Hood is optional (not included in the box). This (arguably over-priced) lens hood features a bayonet mount with a release button that is a very nice upgrade from the 50mm f/1.8 II's threaded adapter and hood combination. This is a flat-topped, rounded hood that does not extend with focusing and adds a nice amount of protection to the already deep-set objective lens. Access to the front-set focus ring is slightly more difficult with the lens hood in place.
No case is included in the box, but finding somewhere to stow this lens should not be challenging. Canon's recommended case is the
LP1014. This is a modestly protective drawstring pouch, but it is rather pricey. A small
Lowepro Lens Case costs far less, offers better protection and has more functionality.
Price and Value
Creating few arguments is the price of the Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens as it is the lowest priced Canon lens available. It is hard not to like that fact.
More arguable is the value of this lens.
Photographer's opinions of this lens seem to be polarized. Some don't understand why it exists, saying that lenses such as the
Canon EF-S 18-135mm f/3.5-5.6 IS STM Lens are more versatile and offer a better value (albeit at a higher price). Others think the 50 STM is a great addition to the kit for the price. That this is Canon's best-selling lens as of review time reflects the latter opinion being prevalent.
While this lens is not going to be high on the wish list for most professional and serious amateur photographers, the value it offers will land this lens in some of those kits. Even if it does not get frequent use, the 50 f/1.8 STM makes a very inexpensive backup lens that will barely be noticed in the bag.
The tested 50mm f/1.8 STM lens was retail-sourced.
Alternatives to the Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens
Alternatives to the Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens abound. There are many prime lens options and far more zoom lens options.
The most-similar alternative to the 50 f/1.8 STM is the lens it is replacing in Canon's lineup, the
EF 50mm f/1.8 II Lens. Usually, Canon introduces lenses that are replacing previous models with a noticeably higher price and that higher price usually preserves photographers' investment in the previous version. Breaking tradition, the 50 f/1.8 STM lens wears the same price tag as the 50 f/1.8 II version, a move that will certainly devalue the prior version. Still, the f/1.8 II investment was very small and the value reduction will not be strongly felt by most.
The physical differences between these lenses are listed in the bullet points at the beginning of this review. They are numerous and of significance.
An
image quality comparison shows the news lens to be sharper in the center at f/1.8, transitioning to be more-noticeably sharper in the corners at f/4 and narrower. You might notice slightly less flare from the STM.
The bottom line is that, unless you get a fabulous deal on the II and your budget is rock bottom, the STM is a much better choice. For those considering the upgrade from the II to the STM, I say go for it.
The next alternative I'll mention is the 22-year-older (overdue for an update), 2/3-stop wider
Canon EF 50mm f/1.4 USM Lens. From an
image quality perspective, the 50mm f/1.4 is slightly sharper in the center of the frame at a comparable f/1.8 aperture through f/2.8 or f/4. At f/4, the f/1.8 lens takes the lead in the corners. Beyond f/4, it doesn't matter which lens you choose (in regards to sharpness).
The f/1.4 is modestly larger and nearly twice as heavy. The f/1.4 has an extra element, group and aperture blade. The f/1.4 has USM AF, but ... it is a micro USM implementation (vs. Ring USM). The f/1.4 has a focus distance window.
The f/1.8 STM price is less than 1/3 of the f/1.4's price with no rebates factored in. I'm sure that last sentence will finish off the decision for many.
That the 50mm f/1.8 STM has a 1 1/3 stop aperture advantage is worth mentioning. The 50 will show less vignetting at f/2.8 and it has slightly less distortion. The 40 STM is shorter and slightly lighter, has one less group. The 40 focuses slightly closer but with a wider focal length, has a slightly lower maximum magnification. The 40 STM has a higher list price, but the difference is worth checking as rebates can cut this difference significantly.
Summary
It is easy to love a lens with perfect optical quality, best-available AF and first-class build quality. Start dropping any of those attributes and size, weight and price concessions are expected with the amount of the price concession being the all-important factor for many. In this case, the price concession is very substantial, easily making the 50 STM Canon's lowest priced lens. This ultra-low price, combined with an extremely light weight (only Canon's pancake lenses and the 50mm f/1.8 II are lighter), very small size (only Canon's pancake lenses are shorter) and impressive stopped down image sharpness, immediately (and unsurprisingly) launched the Canon EF 50mm f/1.8 STM Lens to the pinnacle of Canon's best seller list.